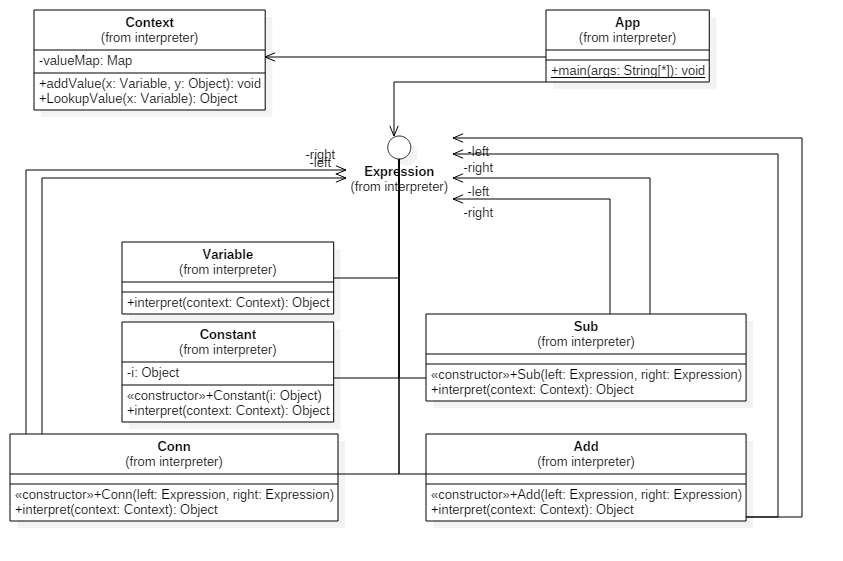
public interface Expression {
Object interpret(Context context);
}
public class Add implements Expression {
private Expression left;
private Expression right;
public Add(Expression left, Expression right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public Object interpret(Context context) {
return left.interpret(context).equals("CPU") && right.interpret(context).equals("Memory") ?
"主板" :
left.interpret(context).equals("Memory") && right.interpret(context).equals("CPU") ?
"主板" :
left.interpret(context).equals("主板") && right.interpret(context)
.equals("显示器") ? "电脑" : "四不像";
}
}
public class Sub implements Expression {
private Expression left;
private Expression right;
public Sub(Expression left, Expression right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public Object interpret(Context context) {
return left.interpret(context).equals("主板") && right.interpret(context).equals("CPU") ?
"Memory" :
right.interpret(context).equals("Memory") ? "CPU" : "四不像";
}
}
public class Conn implements Expression {
private Expression left;
private Expression right;
public Conn(Expression left, Expression right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public Object interpret(Context context) {
return left.interpret(context).equals("电脑") && right.interpret(context).equals("电源") ?
"生产力" :
"废铁";
}
}
public class Variable implements Expression{
@Override
public Object interpret(Context context){
return context.LookupValue(this);
}
}
class Constant implements Expression {
private Object i;
public Constant(Object i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public Object interpret(Context context) {
return i;
}
}
public class Context {
private Map valueMap = new HashMap<>();
public void addValue(Variable x, Object y) {
valueMap.put(x, y);
}
public Object LookupValue(Variable x) {
return valueMap.get(x);
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Variable cpu = new Variable();
Variable mem = new Variable();
Variable ele = new Variable();
Constant screen = new Constant("显示器");
Context context = new Context();
context.addValue(cpu, "CPU");
context.addValue(mem, "Memory");
context.addValue(ele, "电源");
Expression expression = new Conn(
new Add(
new Add(
new Sub(
new Add(cpu, mem)
, cpu)
, cpu)
, screen)
, ele);
System.out.println(expression.interpret(context));
}
}