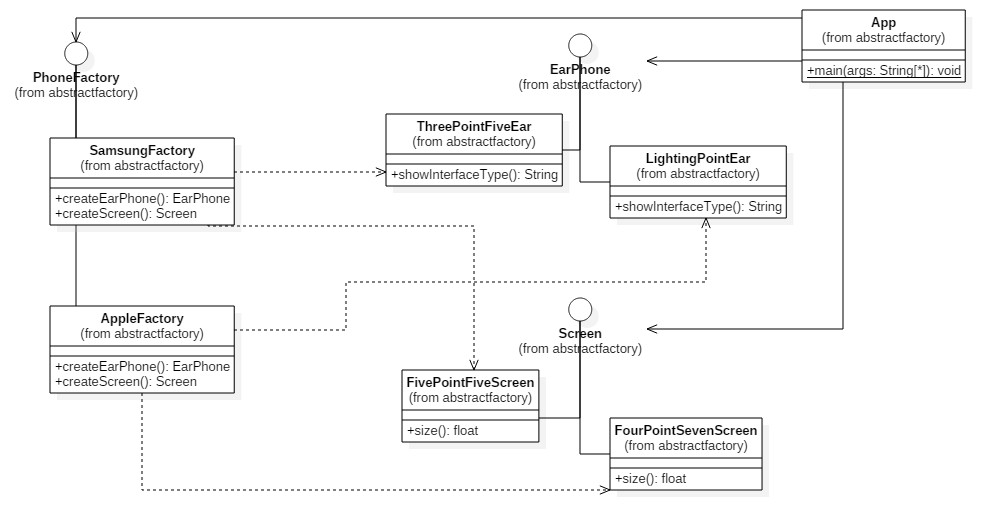
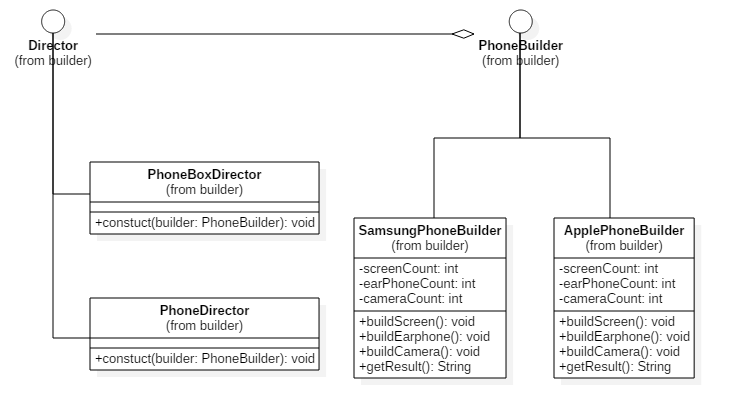
public interface PhoneBuilder {
void buildScreen();
void buildEarphone();
void buildCamera();
String getResult();
}
public class ApplePhoneBuilder implements PhoneBuilder {
private int screenCount;
private int earPhoneCount;
private int cameraCount;
@Override public void buildScreen() {
System.out.println("构建苹果屏幕");
screenCount++;
}
@Override public void buildEarphone() {
System.out.println("构建苹果耳机");
earPhoneCount++;
}
@Override public void buildCamera() {
System.out.println("构建苹果摄像头");
cameraCount++;
}
@Override public String getResult() {
return "苹果手机构建完成,组件数量:"+screenCount+" "+earPhoneCount+" "+cameraCount;
}
}
public class SamsungPhoneBuilder implements PhoneBuilder {
private int screenCount;
private int earPhoneCount;
private int cameraCount;
@Override public void buildScreen() {
System.out.println("构建三星屏幕");
screenCount++;
}
@Override public void buildEarphone() {
System.out.println("构建三星耳机");
earPhoneCount++;
}
@Override public void buildCamera() {
System.out.println("构建三星摄像头");
cameraCount++;
}
@Override public String getResult() {
return "三星手机构建完成,组件数量:" + screenCount + " " + earPhoneCount + " " + cameraCount;
}
}