Factory Method(工厂方法)
工厂方法模式
- 定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类,使一个类的实例化延迟到子类
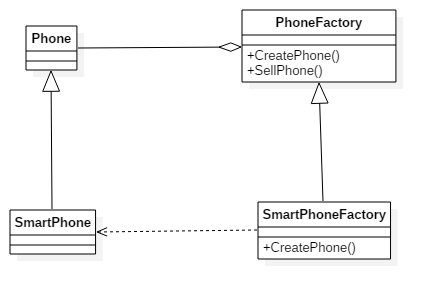
- 一个手机
|
|
- 手机工厂
|
|
- 智能手机
|
|
- 智能手机工厂
|
|
- 客户端
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1、可以尝试非阻塞获取锁(lockInterruptibly())
2、能被中断地获取锁
3、超时获取锁
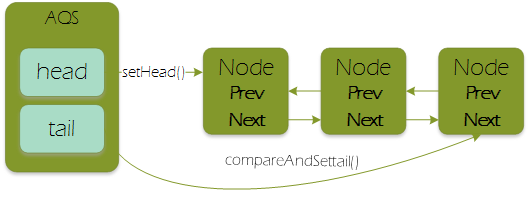
通过几个死循环的方式保证节点添加的并发请求串行化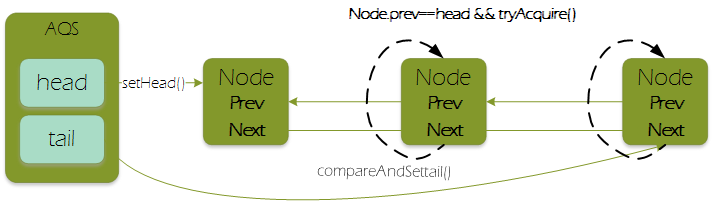
节点进入同步队列后,自省观察并获取同步状态,过程中头节点不为空,enq方法保证,第一次enq方法后(enq中会有两次循环),队列状态如下:
入参节点node的前驱是一个新节点,在方法enq中new出,此时新的线程在公平锁的获取流程中,hasQueuedPredecessors()返回ture,后继节点node再继续获取锁的流程中(注意此时图中node的线程并没有返回,因而获取锁过程没有结束),多个线程竞争依靠compareAndSetState的CAS方式保证一致性。

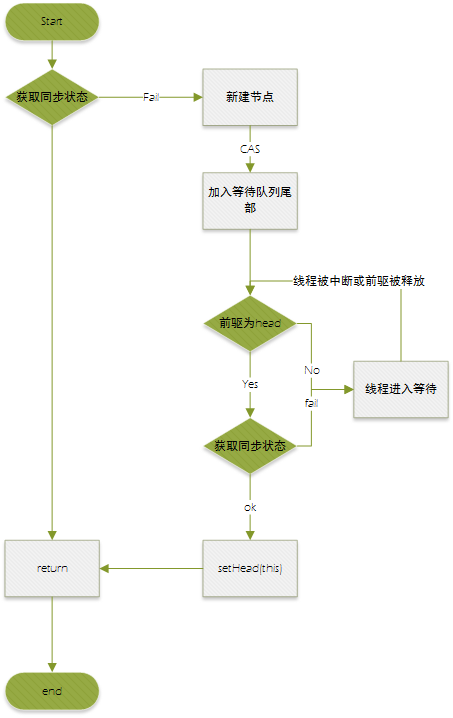
释放调用release(int)方法进行释放,其中唤醒后继节点
|
|
测试代码:
1、获取同步状态时,如果该线程与当前持有线程相同,则进行同步状态值增加返回true,表示获取成功
2、公平锁与非公平锁:前者FIFO(获取锁时会检查当前同步队列时候有等待的线程节点,见上文红色),后者CAS竞争,前者代价是进行大量的线程切换(切换锁),非公平锁可能造成饥饿,但是线程切换很少(耗时94倍,切换次数133倍)
1、同一时刻允许多个读线程访问,写线程访问时,读写均阻塞
2、一般情况下,读写锁的性能都会比排它锁好,大多数情景读是多于写的
3、读写锁实现分析:整形按位切割,32位前16位用于标记读状态,后16位标记写状态,写状态=S & 0X0000FFFF,读状态=S>>>16,所以,S不等于0时候,写状态=0则读状态>0,即表示读锁已经获取
4、锁降级:把持住写锁,再获取到读锁,随后释放写锁
1、Condition对象:依赖Lock接口实现一套等待通知机制
2、一个示例,有界队列:
3、如果一个线程调用Condition.await(),则其释放锁、构造为节点加入等待队列并进入等待状态
4、等待await:同步队列中的首节点构造为新节点,加入等待队列,等待队列新增节点的线程不需要CAS,因为调用await()的线程必定获取了锁,由锁来保证线程安全
5、通知signal:一起唤醒唤醒等待时间最长的,即首个等待节点,加入同步队列中由locksupport唤醒节点中的线程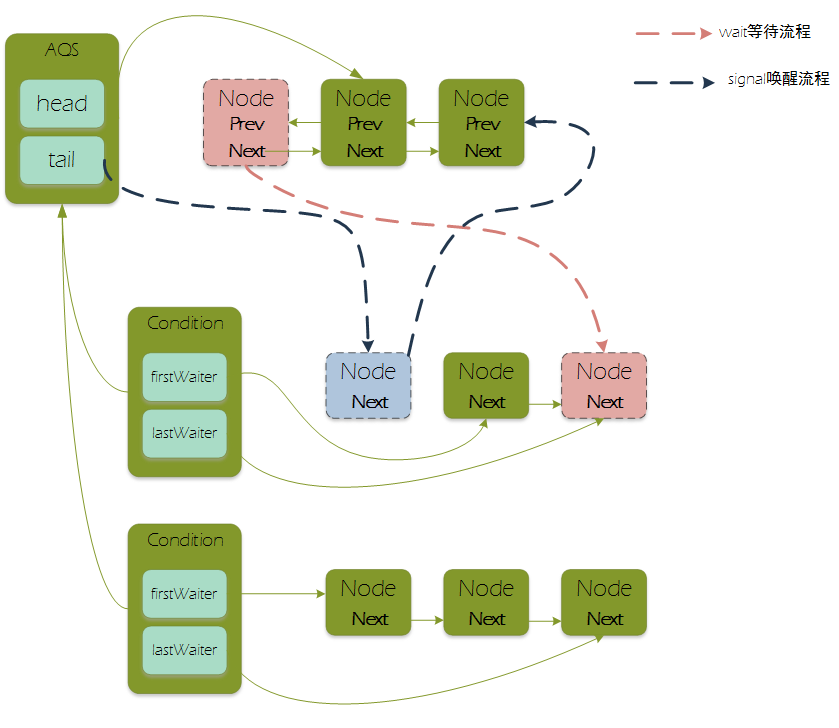
U: 目标CPU使用率 [0,1]
W: wait time
C: compute time
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F: 必须串行部分的比例
N: CPU个数
|
|